产品搜索
结构搜索
全站搜索
当前位置: 行业资讯
新型化合物面世,或可同时治疗两种疾病
2017-02-22
来源:转载自第三方
2017-2-22
近期,来自英国巴斯大学和芬兰奥卢大学的研究人员创造出了一种新型化合物分子,能够增加脂肪细胞葡萄糖的摄入,并抑制结肠癌细胞的生长,有望在未来用于治疗癌症和糖尿病。该研究成果以题为“Highly Potent and Isoform Selective Dual Site Binding Tankyrase/Wnt Signaling Inhibitors That Increase Cellular Glucose Uptake and Have Antiproliferative Activity”[1]的文章,发表于著名学术期刊《Journal of Medicinal Chemistry》上。

图1. JMC发表关于新化合物有望治疗糖尿病和结肠癌的文章。
糖尿病是一种综合性代谢类疾病,根据降糖机制,目前的治疗药物可分为如下几类:磺脲类,如格列本脲、格列美脲等;双胍类,如苯乙双胍、二甲双胍;α-糖苷酶抑制剂,如阿卡波糖、伏格列波糖;胰岛素增敏剂,如罗格列酮、曲格列酮等;GLP-1受体激动剂艾塞那非等;DPP-4抑制剂维格列汀(中间体3-氨基-1-金刚烷醇)等;以及各类胰岛素。而结肠癌的发生、发展是多基因多事件积累的结果,经过多年的研究发现,Wnt信号通路异常激活参与了人类大肠癌的发病。目前,并没有一种药物能够同时治疗这两种疾病。
在本项研究中,英国巴斯大学癌症研究所与芬兰奥卢大学的研究者以8-氨基喹啉为底物合作定制了两种特定性抑制端锚聚合酶的分子。该分子在细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中起重要作用,能够提高脂肪细胞的糖摄取,帮助糖尿病人控制疾病,减少胰岛素的用量;同时抑制结肠癌细胞的增殖和扩散。该化合物有望成为同时治疗癌症和糖尿病的药物。
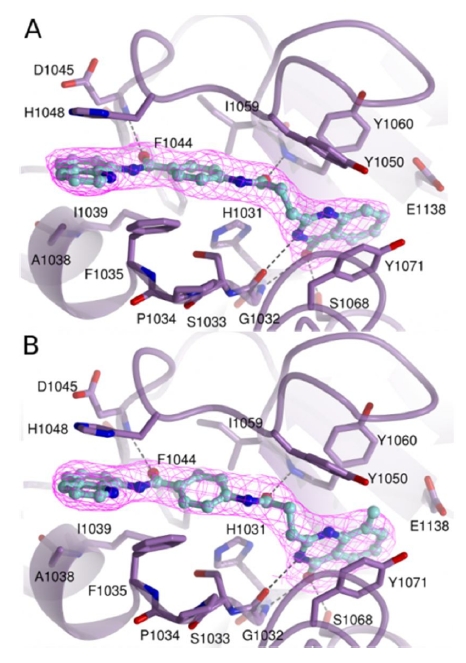
图2. 两种化合物与端锚聚合物酶结合的晶体结构。(图片来自原文)
虽然现在讲该新型分子制成的药物能够同时治疗糖尿病和结肠癌以及其他炎性肿瘤似乎还为时尚早,但这是一个重要的开端。下一步,研究者将进一步优化该化合物分子,并利用特定模型等来评估其药效,进一步研究开展可能治疗方案的机会。他们计划利用癌症患者的细胞开发出一个3D模型,来更好的理解该端锚聚合物酶/Wnt信号通路抑制剂;同时利用肥胖和糖尿病的生物模型来调查脂肪细胞的减少和对胰岛素敏感度的提高作用。
据国际糖尿病联盟去年公布的数据显示,目前全球共有超过4.5亿人口受糖尿病困扰,到2025年,全球约有1.75亿患者,到2040年,将有约6.42亿患者,糖尿病容易引起其他如肥胖、心血管疾病等并发症;而癌症也会影响身体各系统的功能,比手术和化疗更好的治疗方法将给患者的身体和精神都带来极大的益处。因此,能够同时治疗这两种疾病的药物的开发对社会和患者都具有重大的意义。
参考文献
[1] Amit Nathubhai, Teemu Haikarainen, Jarkko Koivunen, et al. Highly Potent and Isoform Selective Dual Site Binding Tankyrase/Wnt Signaling Inhibitors That Increase Cellular Glucose Uptake and Have Antiproliferative Activity. J. Med. Chem., 2017, 60(2), pp. 814–820.
相关链接:3-氨基-1-金刚烷醇
1,1-二甲双胍盐酸盐
8-氨基喹啉
1,1-二甲双胍盐酸盐
8-氨基喹啉
本文由苏州亚科科技股份有限公司编辑
如果涉及转载授权,请联系我们。